Keeping your blood sugar levels stable is one of the most important steps toward protecting your long-term health. Whether you’re living with diabetes, managing prediabetes, or simply trying to support a healthier lifestyle, the foods you eat play a major role in how your body processes glucose. The right food choices can prevent spikes, promote better insulin sensitivity, reduce inflammation, and keep your energy steady throughout the day.
In this guide, we break down the Top 15 Best Foods That Lower Blood Sugar, along with why they work and how you can incorporate them into everyday meals. If you’ve been looking for simple, natural ways to support your health, these foods offer powerful benefits backed by nutrition science.
Why Food Choices Matter for Blood Sugar Control
Before exploring the list, it’s important to understand how food affects blood sugar. When you eat carbohydrates, your body breaks them down into glucose. The speed at which this glucose enters the bloodstream depends on:
- Fiber content
- Natural sugars vs processed sugars
- Presence of protein and healthy fats
- How refined or whole the food is
Foods high in refined carbs or sugar get absorbed quickly, causing sudden spikes. In contrast, foods rich in fiber, healthy fats, and protein digest slower and release sugar more steadily.
Now let’s dive into the list of foods that naturally support healthier blood sugar levels.
15 Best Foods That Lower Blood Sugar
1. Oats
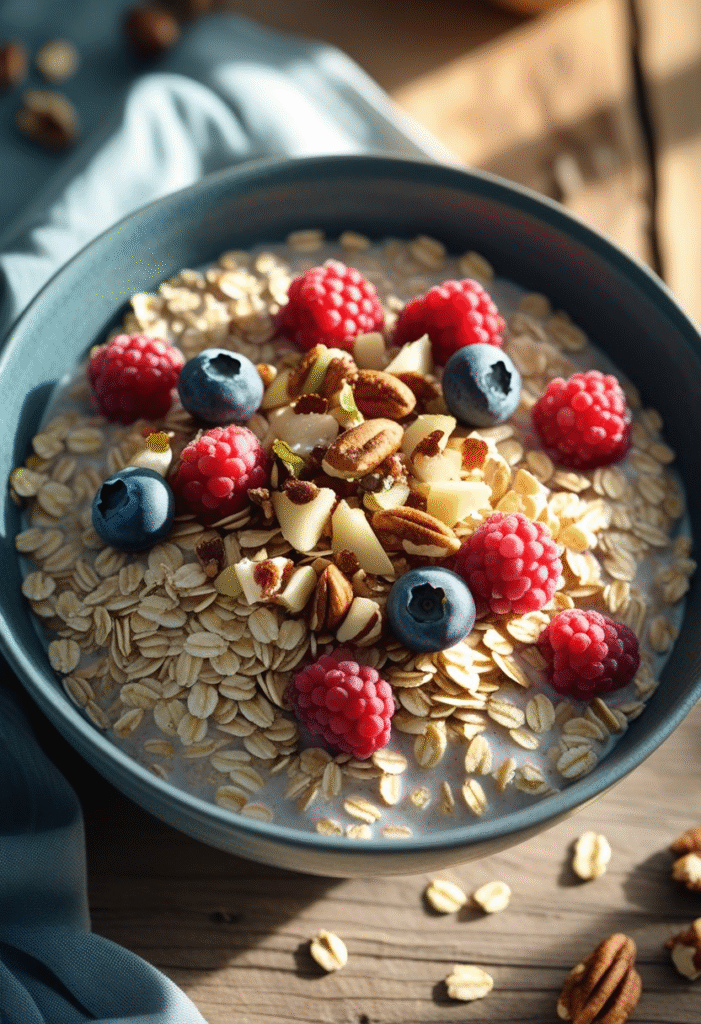

Oats are a nutrient-dense powerhouse loaded with beta-glucan, a type of soluble fiber that slows digestion and sugar absorption. This makes oats one of the best breakfast options for maintaining stable glucose. Choose steel-cut or rolled oats, as instant varieties are more processed and may spike sugar levels quicker.
How to eat it:
Add nuts, berries, and cinnamon for a blood sugar–friendly meal.
2. Leafy Green Vegetables
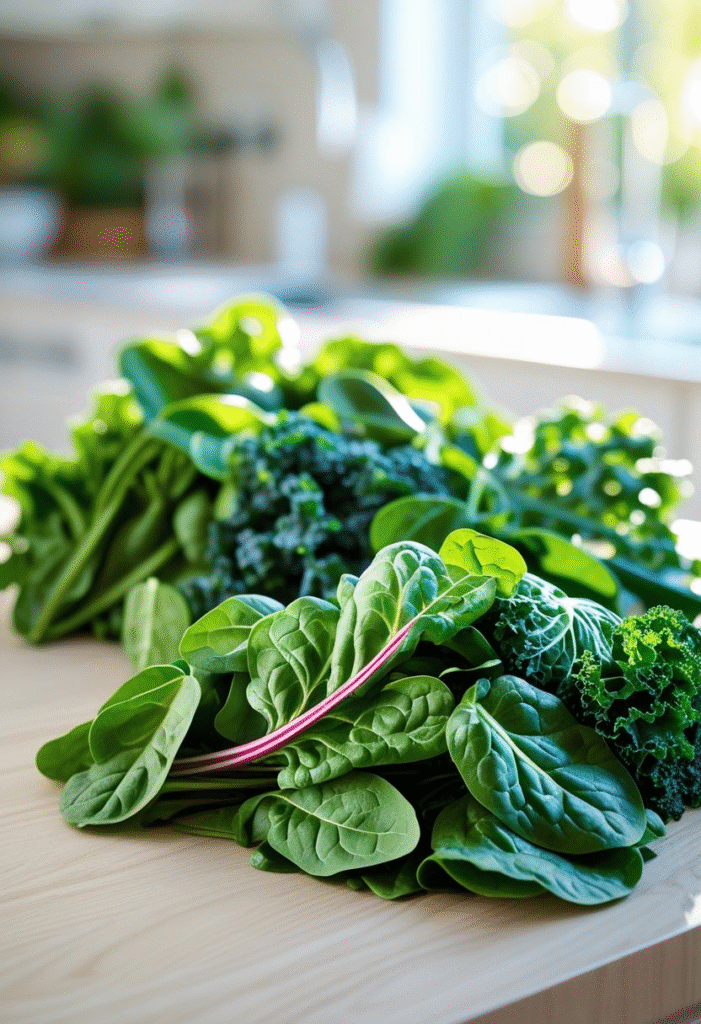

Spinach, kale, collard greens, and Swiss chard are extremely low in carbohydrates and packed with magnesium—a mineral linked to improved insulin sensitivity. They’re also rich in antioxidants that reduce inflammation, which is crucial for people managing diabetes.
How to eat it:
Add them to salads, smoothies, soups, and omelets.
3. Berries
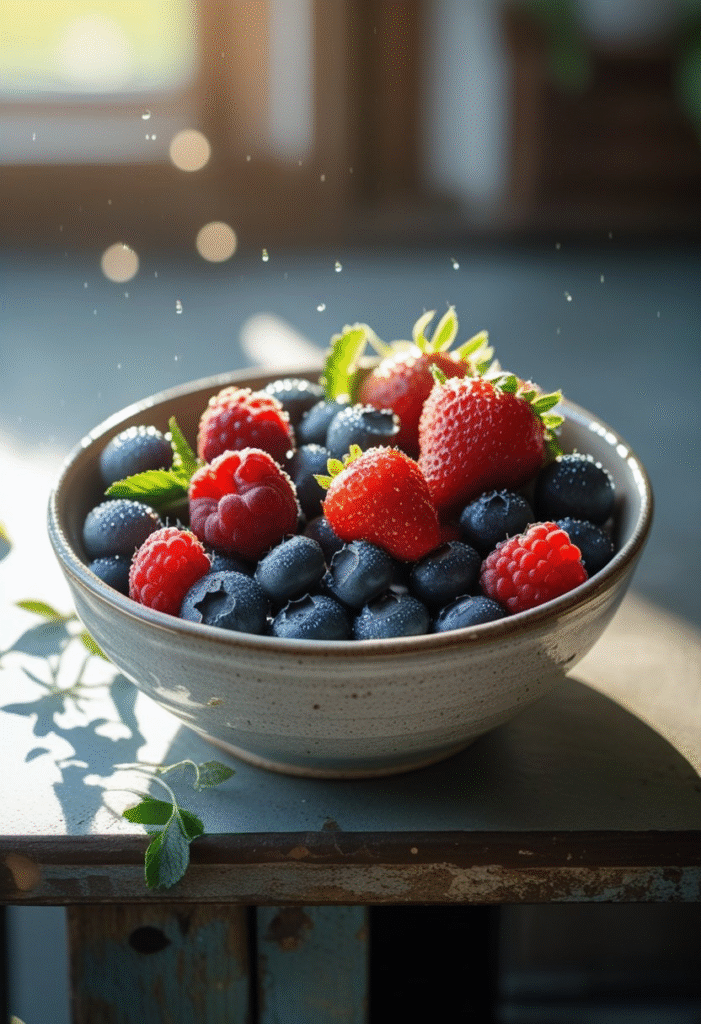
Fruit lovers don’t have to miss out. Berries like blueberries, strawberries, raspberries, and blackberries offer sweetness with less sugar than other fruits. Their high fiber and antioxidant levels help reduce glucose spikes after meals.
How to eat it:
Mix berries into yogurt, salads, or oatmeal.
4. Beans and Lentils
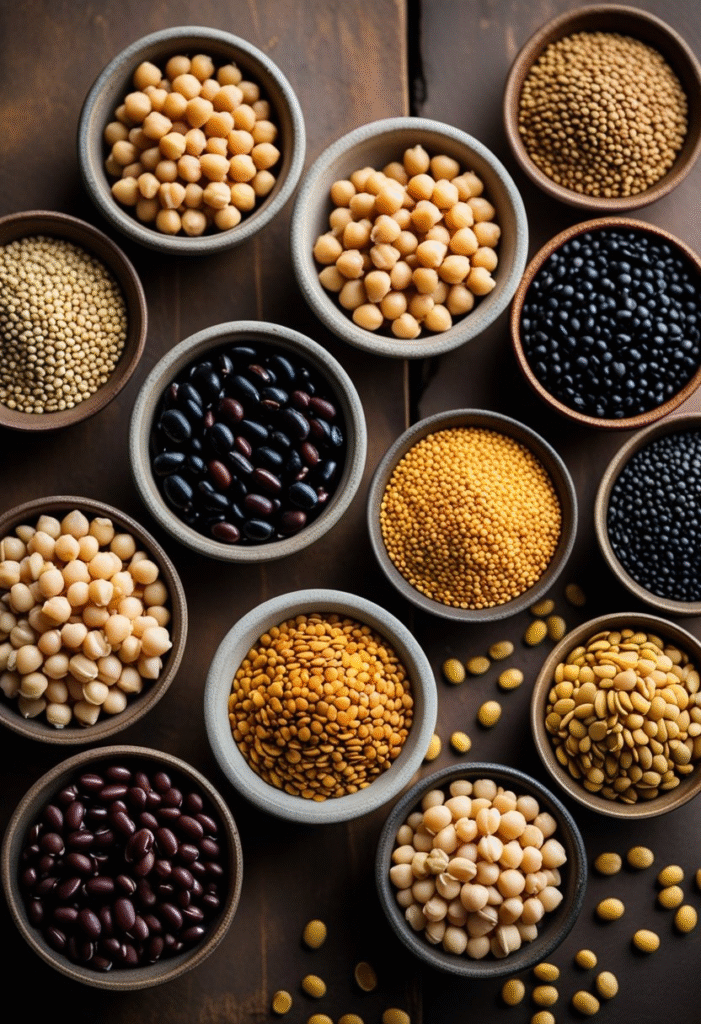

Lentils, chickpeas, and various types of beans digest slowly due to their rich combination of fiber and plant protein. They keep you full longer, prevent cravings, and support steady blood sugar release.
How to eat it:
Use them in soups, stews, chili bowls, wraps, or salads.
5. Greek Yogurt
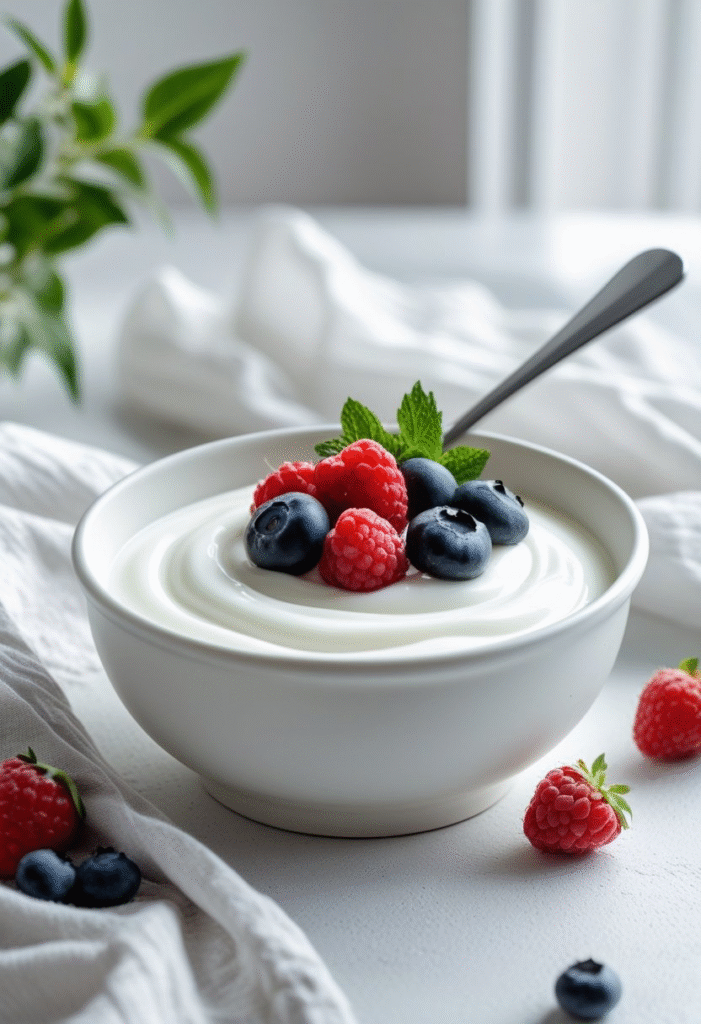

Plain Greek yogurt contains probiotics that improve gut health—something strongly connected to blood sugar control. It also contains more protein and fewer carbs than regular yogurt, making it perfect for balanced snacking.
How to eat it:
Top it with nuts or berries, or use it as a base for smoothies.
6. Nuts and Seeds
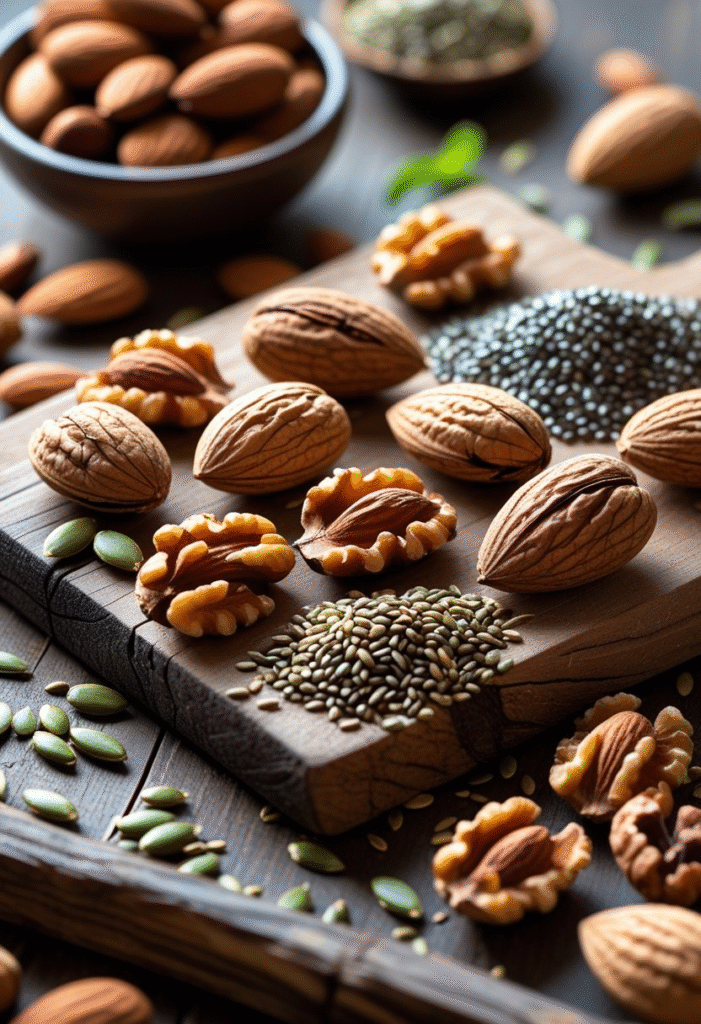

Almonds, walnuts, cashews, chia seeds, flaxseeds, and pumpkin seeds all help reduce blood sugar spikes thanks to their blend of healthy fats, protein, and fiber. They also reduce inflammation and support heart health—a major benefit for people with diabetes.
How to eat it:
Add them to salads, oatmeal, yogurt bowls, or smoothies.
7. Cinnamon
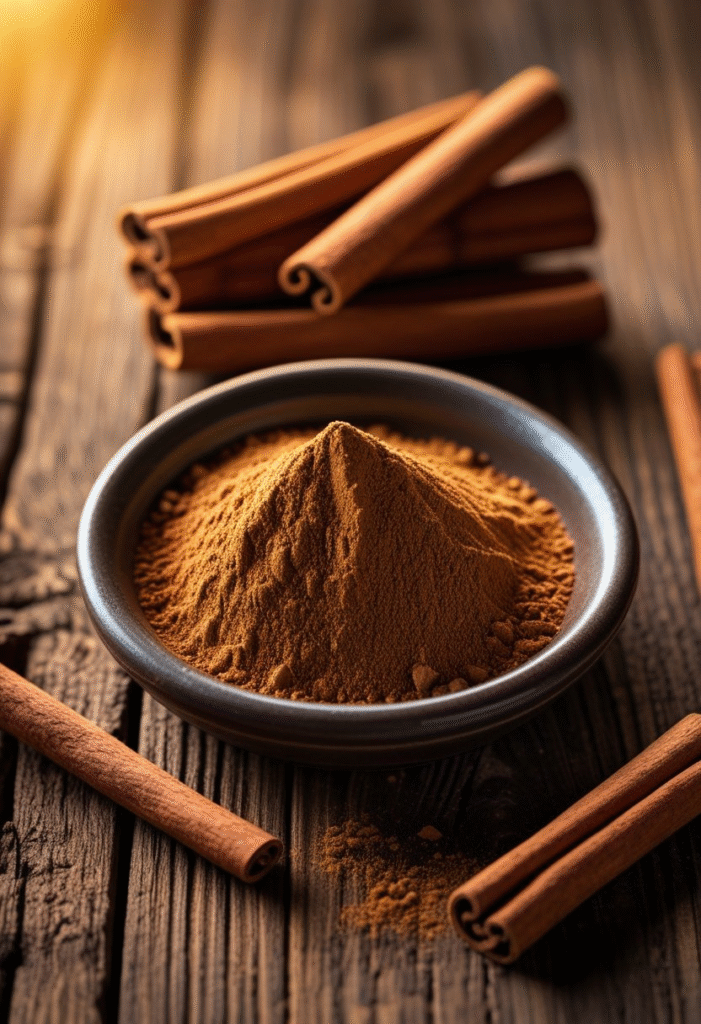

Although technically a spice, cinnamon deserves a place on this list. It contains natural compounds that may mimic insulin’s role in the body and improve your cells’ ability to absorb glucose. Even small daily amounts can support better blood sugar levels.
How to eat it:
Sprinkle on oatmeal, tea, coffee, or baked sweet potatoes.
8. Fatty Fish
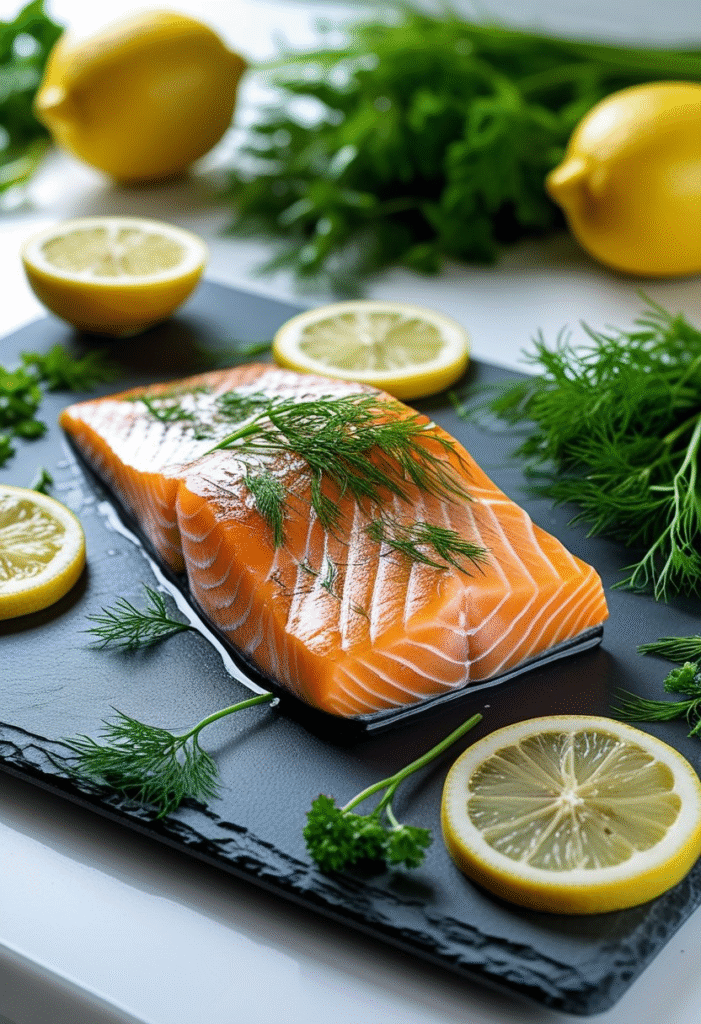

Salmon, sardines, herring, tuna, and mackerel offer omega-3 fatty acids that reduce inflammation and improve insulin response. These fish also stabilize blood sugar by providing high-quality protein without raising carbohydrate levels.
How to eat it:
Bake, grill, or pan-sear fatty fish and pair with leafy greens for a balanced meal.
9. Avocados
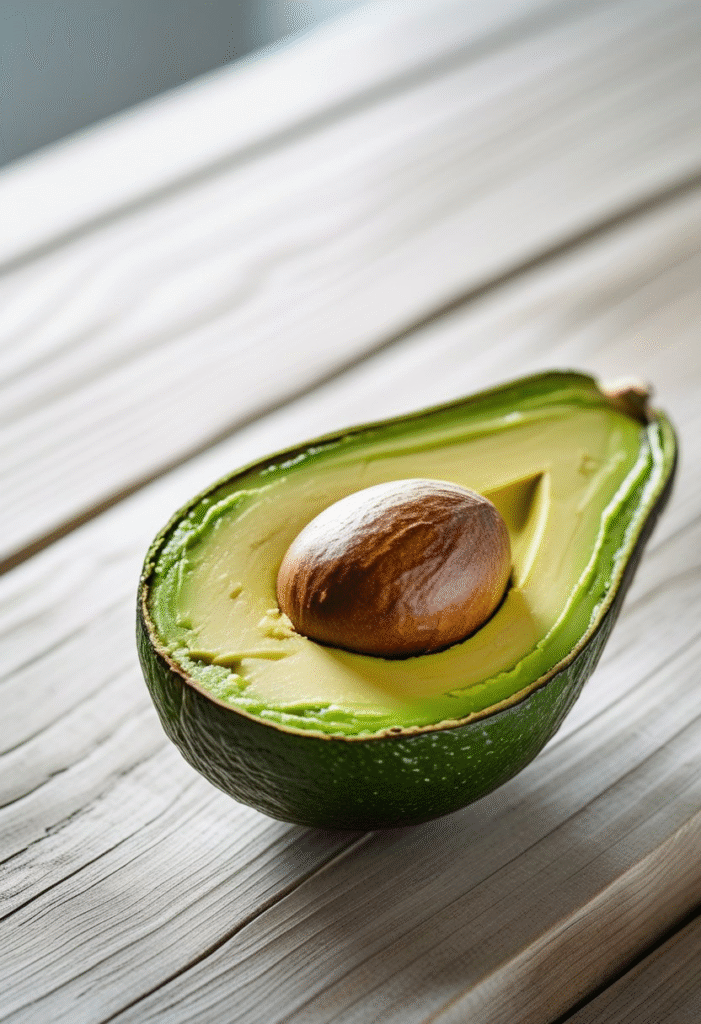

Avocados contain monounsaturated fats and fiber that keep you full and prevent sugar spikes. They also promote healthy cholesterol levels, making them an excellent choice for people with metabolic health concerns.
How to eat it:
Spread on whole-grain toast, add to salads, or blend into smoothies.
10. Eggs
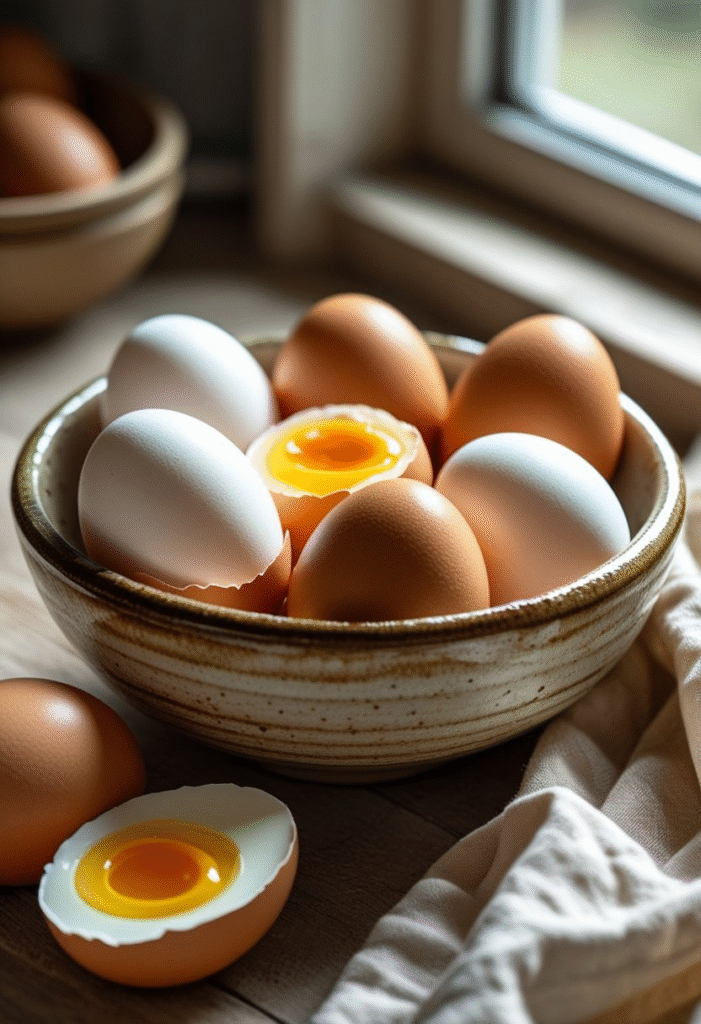

Eggs are naturally low in carbs and rich in protein, which keeps blood sugar steady. They also contain healthy fats and essential nutrients like choline. Eating eggs for breakfast has been shown to reduce glucose fluctuations throughout the day.
How to eat it:
Boiled, scrambled, poached, or as a veggie-packed omelet.
11. Whole Grains
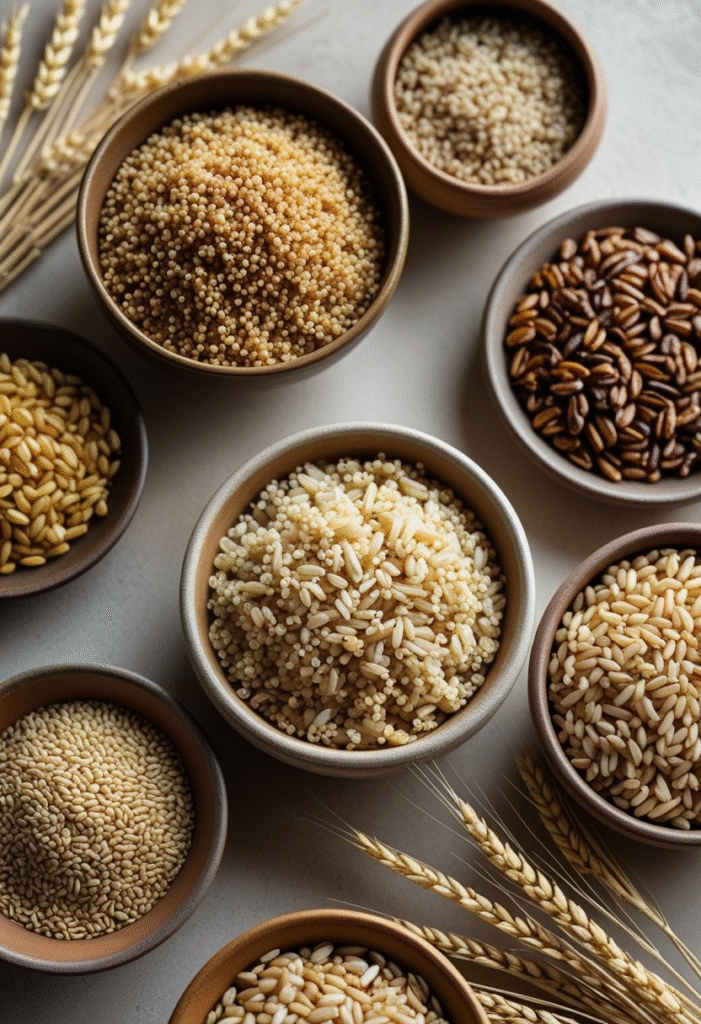

Whole grains like quinoa, brown rice, barley, bulgur wheat, and whole-grain bread have more fiber and nutrients compared to refined grains. They digest slower, preventing glucose spikes while helping you stay full longer.
How to eat it:
Replace white rice with quinoa or barley, and choose whole-grain breads.
12. Broccoli and Cruciferous Vegetables
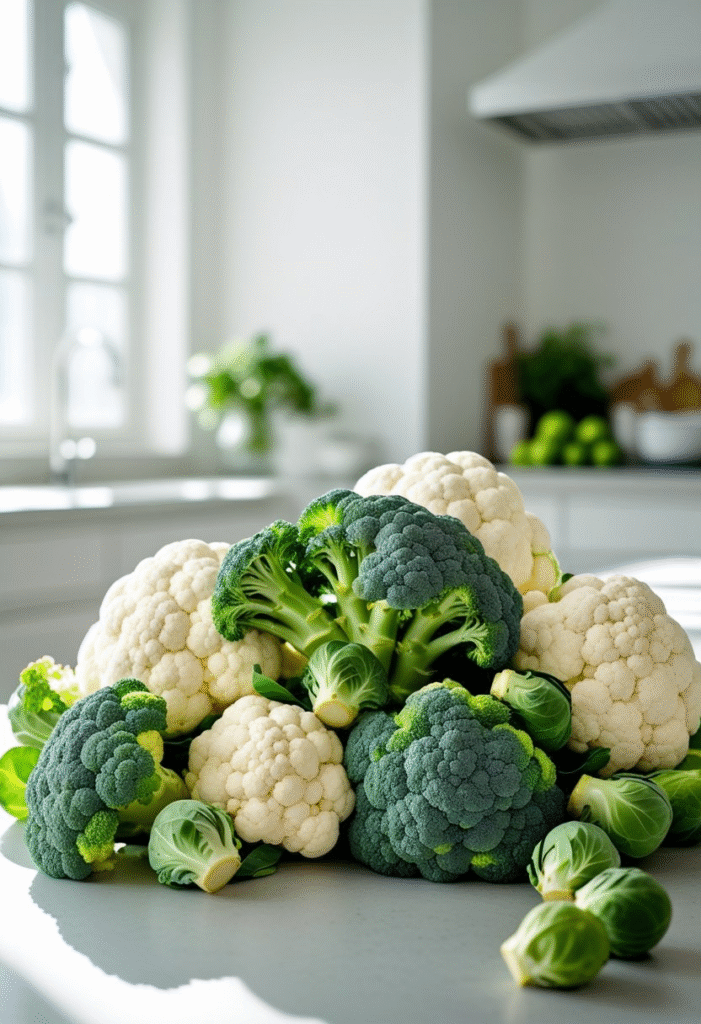

Broccoli, cauliflower, cabbage, and Brussels sprouts contain sulforaphane, a compound that may reduce blood sugar and improve insulin resistance. They are also low in carbs and calories, allowing you to eat them generously.
How to eat it:
Steam, roast, add to stir-fries, or blend into soups.
13. Garlic
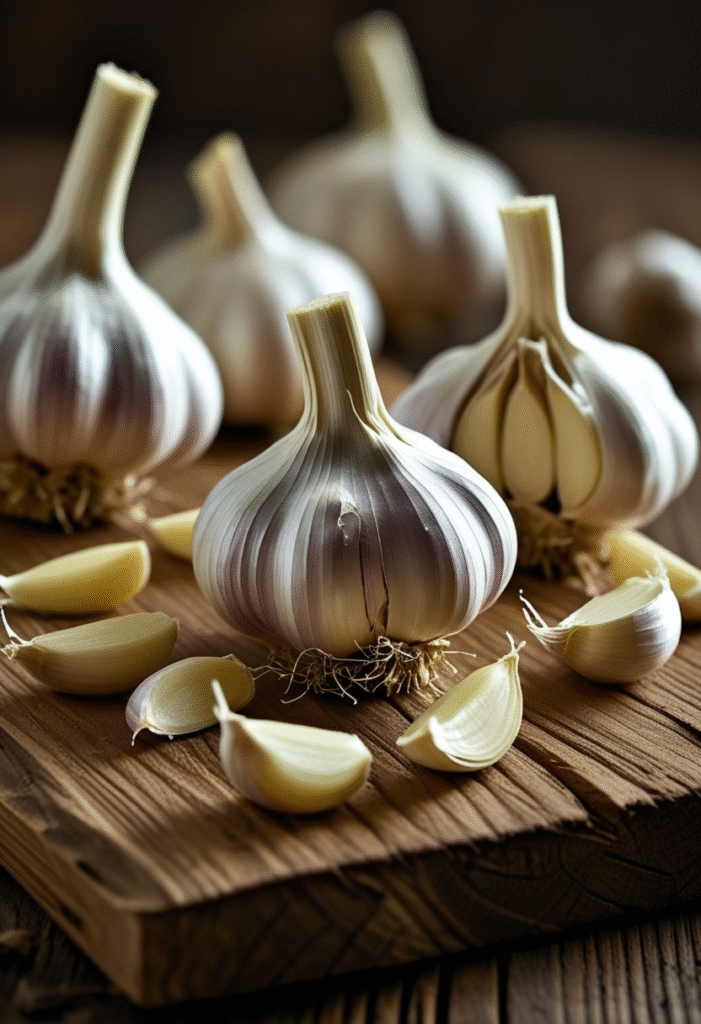

Garlic is known for boosting immunity, but it also supports blood sugar control by improving insulin sensitivity. Its anti-inflammatory properties also benefit metabolic health.
How to eat it:
Add fresh garlic to sauces, soups, curries, and roasted vegetables.
14. Apple Cider Vinegar
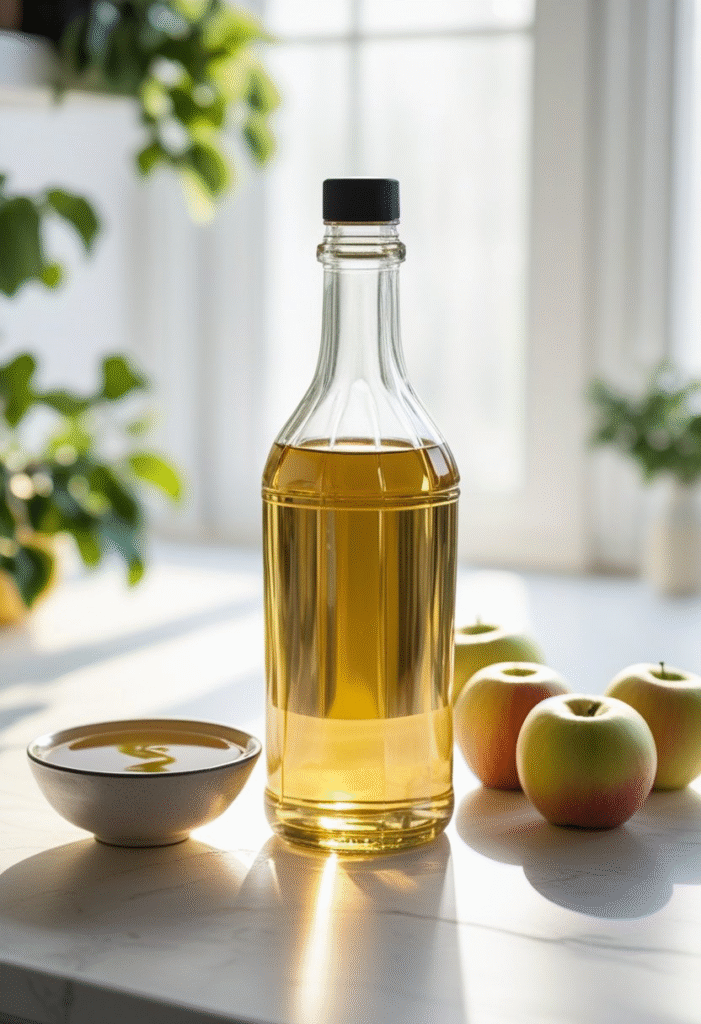

Apple cider vinegar (ACV) slows stomach emptying and improves insulin function, making it useful for reducing post-meal glucose spikes. Many studies show that drinking ACV before meals can significantly reduce blood sugar levels.
How to consume:
Mix 1–2 tablespoons with water before meals.
Always dilute to protect your teeth and digestion.
15. Sweet Potatoes
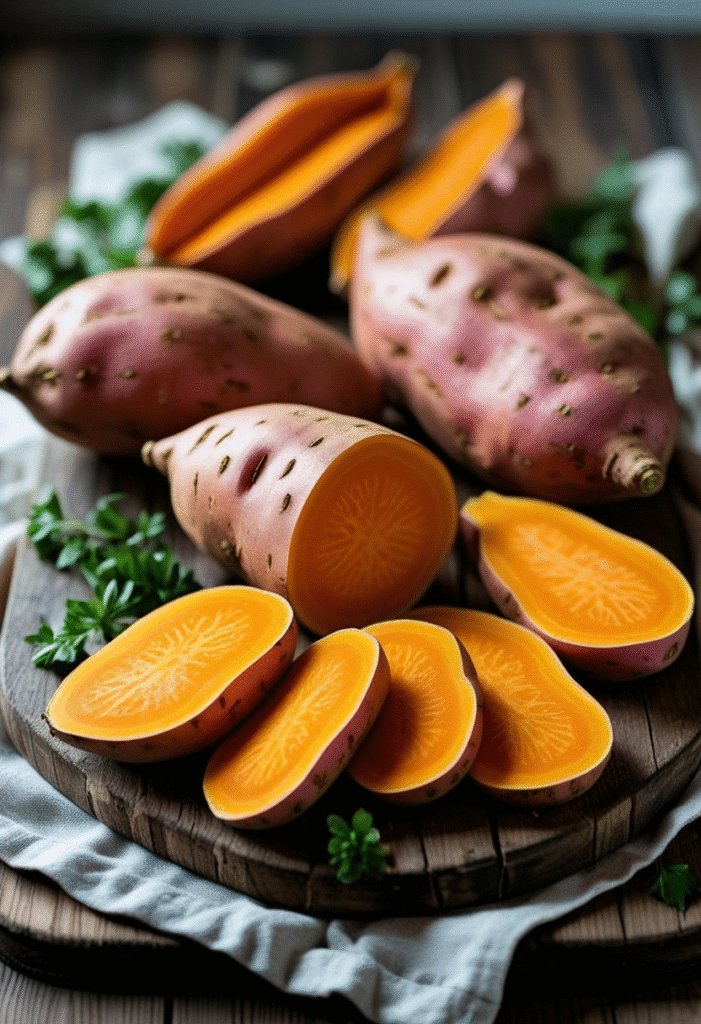
Sweet potatoes release sugar slowly into the bloodstream thanks to their low glycemic index and high fiber content. They also contain B vitamins, potassium, and antioxidants that support healthy metabolism.
How to eat it:
Bake, roast, or air fry them for a nutritious side dish.
How to Incorporate These Foods into Your Routine
Adding these foods to your diet doesn’t require a complete lifestyle overhaul. Simple changes can make a big difference:
- Swap sugary snacks for nuts or berries.
- Use avocado instead of butter or mayo.
- Choose whole grains over refined grains.
- Drink diluted ACV before carb-heavy meals.
- Add cinnamon to beverages or breakfast foods.
- Include beans, lentils, or greens in at least one meal daily.
Consistency is more important than perfection.
Additional Tips for Managing Blood Sugar Naturally
Along with choosing foods that support stable glucose levels, these habits can amplify results:
1. Stay Hydrated
Water helps the kidneys flush out extra sugar and prevents dehydration spikes.
2. Move After Meals
Even a 10–15 minute walk improves insulin sensitivity.
3. Control Portion Sizes
Large meals can cause sudden sugar surges.
4. Avoid Excessive Processed Sugars
Limit pastries, sugary drinks, and white bread.
5. Get Enough Sleep
Poor sleep affects hunger hormones and raises blood sugar.
Final Thoughts
Choosing the right foods plays a powerful role in supporting long-term blood sugar balance. Incorporating the Top 15 Best Foods That Lower Blood Sugar into your meals can help you maintain steady energy, reduce cravings, and support overall metabolic health. Whether you are managing diabetes or simply pursuing a healthier lifestyle, these foods offer simple, natural, and delicious ways to take control of your well-being.